
Alternative species (click on the thumbnail to see the card)
Names
Scientific name
Ambastaia sidthimunki
Yasuhikotakia sidthimunki (ancien)
Common name
Dwarf loach
Ladderback loach
Pygmy loach
Chain loach
Chain botia
Origin
Origin: Thailand
Biotope: Asian
Dimorphism

Hardly visible. Females are more rounded and slightly smaller than males.
Group
Cobitidae (Botiidae)
Volume
120 L / 26 Imp Gal / 32 US Gal
Parameters
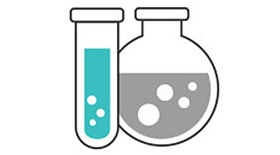
T°: 25 to 26°C or 77 to 79°F
pH: 6.5 to 7
Hardness: 5 to 12°dGH
Difficulty

Easy
Size

4 to 5cm (1.6 to 2")
Longevity

8 to 12 years
Living zone
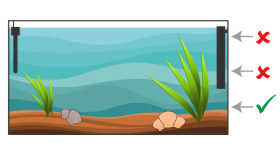
Depth
Individuals
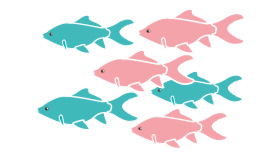
6
Food
How to feed the Dwarf loach?
Food
How to feed the Dwarf loach?
Easy to feed, this loche will easily accept all types of food that you will propose to him.
It will occasionally feed on invertebrates in your aquarium such as snails. However, it needs to be fed specifically to maintain good health. Dwarf lochs are mainly carnivorous and will enjoy prey such as mud worms, tubifex and mosquito larvae.
Rather than offering one large meal a day, we advise you to make several small meals a day for this species. This corresponds much better to their biological rhythm. Therefore, provide 5 or 6 small meals a day.
Be careful, Botias are often sold as a miracle solution to snail overgrowth in the aquarium. So on this subject, indeed they will be able to tackle it but this is not a valid reason for their acquisition. You must review the balance of your aquarium and find the cause of this proliferation. Moreover, fish are living beings that should never be bought for their "usefulness" but because you want to give them a life that suits them.
Behavior
What kind of behavior does the Dwarf loach have?
Behavior
What kind of behavior does the Dwarf loach have?
Dwarf Loaches have a good character and are quite peaceful. They have excellent inter- and intraspecific relationships. Very active and quite lively, they keep busy all day long by staying close to the bottom (they can sometimes be observed swimming in open water with other fish). They alternate phases of intense activity with moments of well-deserved rest! Their main activity consists of frenetically searching the ground in search of potential prey. Their activity is particularly heightened at nightfall.
Fearful, they are reassured by the presence of numerous hiding places (see "its aquarium"). The more hiding places there are, the safer they will feel and the more they will show themselves!
Cohabitation
Who can live with the Dwarf loach?
Cohabitation
Who can live with the Dwarf loach?
Very sociable, this fish will need the presence of its fellow fish to lead a fulfilling life. The minimum requirement is 6 individuals, but if the volume of your aquarium allows it, take more! Thus, a group of 10 individuals is particularly recommended. A social hierarchy will be established, sometimes with a few hours, but not very seriously. In sufficient numbers, they will group together to swim in a school. Some aquarists will even tell you that these loches are playful and mischievous! Maintained in too small numbers, this loach will seek the company of other fish, which is really not recommended for it, nor for the other species.

This loach will cohabit easily with all species of small, peaceful fish. Small peaceful Cyprinidae, Gouramis or Colisa will make good roommates.
Invertebrates being the natural prey of the loch, snails and shrimps will serve as meals.
Breeding
How to breed the Dwarf loach?
Breeding
How to breed the Dwarf loach?
Impossible to date for individuals because in the wild even if very rare cases have been reported. In the wild, reproduction is triggered under the condition of an annual migration. The specimens offered for sale come from breeding (use of hormones).
Its aquarium
Which aquarium for the Dwarf loach?
Its aquarium
Which aquarium for the Dwarf loach?
As these fish live close to the bottom, it is imperative that the floor is not sharp so as not to damage their barbels (or even severely mutilate them in some cases). Absolutely avoid all sharp soils such as quartz (which is actually close to glass). Opt instead for fine sand or Loire sand.

For the decor, plant enough but make sure there is enough space for the loggers to search the ground. For an Asian biotope, you can choose Cryptocorynes, Rotala, Hygrophila, Crinum thaianum, Acorus, Limnophila...
Also install roots that will offer hiding places and shade, much appreciated by these fearful fish! The hiding places can also be in the form of crevices in a rocky scree (be careful with the stability of this scenery, stick the stones together if necessary), half-buried pipes, amphoras, coconuts, inverted flower pots... Use non-calcareous rocks so as not to increase the hardness of the water.
On the filtration side, a flow rate of 2 to 3 times the volume of the tank per hour is sufficient. Direct the filter discharge just below the surface to ensure good mixing and good oxygenation of the water. Of course, you should change the water 10 to 20% every week because Botias like clean water.
Limit the lighting as these shy fish do not like strong light. You can also dim the light with floating plants.
You can also use floating plants.
Good To know
Find all additional information!
Good To know
Find all additional information!

There are about 30 Botia, a dozen of which live in our aquariums.
Her 3 pairs of barbels are sensory organs used in the search for food.
Dwarf Loaches have a bony spine under the eye, a real weapon used to extract snails from their shells. This weapon can also be used in defensive mode. In fact, be careful when handling this fish. It can also get stuck in the trunks of the net or pierce the carrying bag (remember to double it).
Quite sensitive to stress, Botias are prone to white spot disease. Don't worry, this disease is easily preventable through gentle acclimatization and adequate living conditions (living in a group, many hiding places...).
For young specimens, confusion with Ambastaia nigrolineata is possible. Botia nigrolineata is much larger in adulthood (12/15cm or 4.8/5.9") and has continuous bars on the flanks. Finally, it has a 4th pair of small barbels.
Yours photos!
Comments
Sort by:
Please login to post comments


