
Alternative species (click on the thumbnail to see the card)
Names
Scientific name
Microsorum pteropus
Common name
Java Fern
Origin
Origin: Southeast Asia, Malaysia, Thailand
Ideal fertilization

CO2: 5-40mg/l
Nitrates (NO3): 10-50mg/l
Phosphates (PO4): 0,1-3mg/l
Potassium (K): 5-30mg/l
Iron (Fe): 0,01-0,5mg/l
Group
Polypodiaceae
Kind

Rhizome
Parameters
T°: 18 to 25°C or 64 to 77°F
pH: 5.5 to 7
Hardness: 1 to 15°dGH
Difficulty

Easy
Lighting
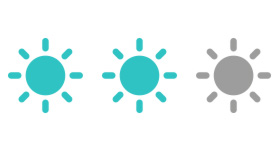
Average
Size

30cm (12")
Plantation
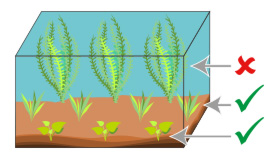
Foreground and Middle
Growth

Slow
Presentation
Who is the Java Fern?
Presentation
Who is the Java Fern?
In its natural environment, the Java fern establishes itself in places where the water level can vary throughout the year. It therefore acclimatizes to a certain degree of drying (leaves out of the water), as well as to total immersion. This asset makes it a versatile plant, available for aquariums, aquaterrariums and paludariums at the same time.
The Java fern has a creeping rhizome. It develops very slowly: some aquarists speak of a leaf every 7 to 10 days.
Microsorum pteropus has an excellent tolerance to the maintenance conditions in your aquarium, so it is ideal for beginner aquarists.
Planting and maintenance
How to plant and maintain the Java Fern?
Planting and maintenance
How to plant and maintain the Java Fern?
You have the choice to install your Microsorum stand in your aquarium. You can plant it in the substrate (do not bury the rhizome in the substrate as it will rot and die), in the foreground or in the middle of your tank. Another solution is to attach it to the decor (rocks or roots) with nylon thread such as fishing line. Once the plant is rooted to its support, you can cut the wire.
In any case, place the plant in the current because this fern likes to be stirred.
Sometimes this plant suffers from necrosis. It then develops brown spots on both sides of its leaves. To remedy the problem, nothing could be simpler: cut off the suffering leaf and remove it from your tub. Be careful, however, as brown spots resembling necrosis may appear on one side of the leaf. In this case, these are spores that the plant produces naturally. Do not cut the leaf.
Farming
How to farm the Java Fern?
Farming
How to farm the Java Fern?
There are two ways to achieve a multiplication of the java fern:
- The first is done naturally: some leaves develop small roots called "seedlings". Let the seedling grow and when it has 2 to 3 leaves, cut it and replant it.
- The second way consists in delicately cutting the rhizome in two, then replanting the two pieces obtained (do not forget to bury only the roots because the total burying of the rhizome causes it to rot).
Good To know
Find all additional information!
Good To know
Find all additional information!
It can be tricky to adapt a Microsorum foot that lives completely submerged to living out of water (from aquarium to paludarium for example). Note that it works much better with seedlings and young shoots that adapt quickly to their new environment.
Yours photos!
Comments
Sort by:
Please login to post comments

